Skin Biopsy
If your doctor is unable to determine the cause of a skin change during a physical evaluation, a skin biopsy might be necessary. Desert Valley Dermatology provides compassionate care for complex skin disorders.
What is a Skin Biopsy Procedure?
Although skin biopsies are typically associated with skin cancer, biopsy procedures might be recommended when other complications are suspected.
A skin biopsy is a diagnostic technique that involves the removal and analysis of a small sample of skin tissue. This procedure is essential for identifying and diagnosing various skin conditions, allowing healthcare professionals to provide appropriate treatment and care to patients.
Types of Skin Biopsy
There are several different types of skin biopsy. The type of skin biopsy procedure your doctor will recommend depends on the location, size, and depth of the suspicious skin growth. Your doctor will also make the determination based on your medical history, symptoms, age, family history, and other relevant details disclosed during your examination.
The types of skin biopsy include the following:
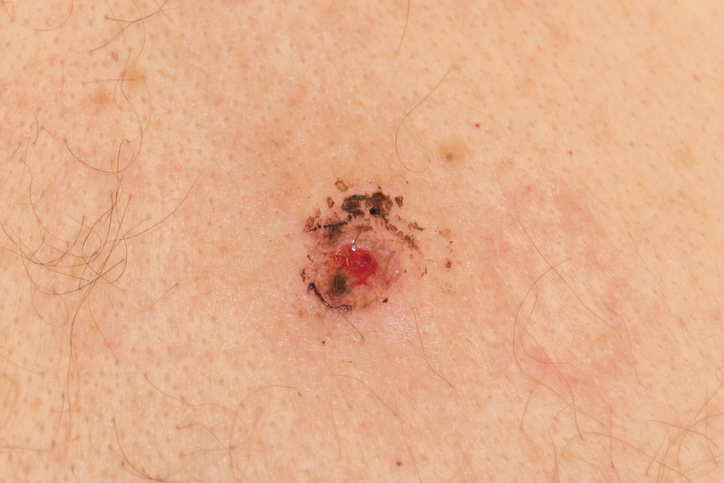
Shave Biopsy
A shave biopsy removes the outermost layers of skin using a scalpel or specialized razor. Shave biopsies are performed when the issue appears to affect only the most surface skin layer. Shave biopsies are typically used to diagnose non-melanoma skin cancers (basal and squamous cell carcinomas), precancerous lesions, and non-cancerous elevated skin growths like skin tags or warts.
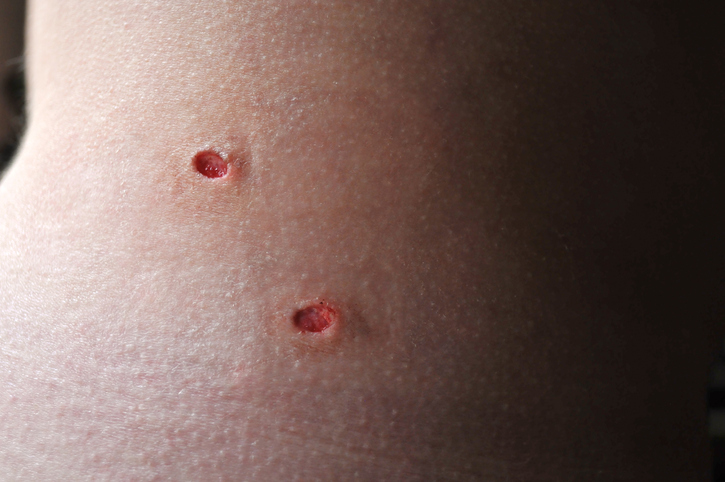
Punch Biopsy
A punch biopsy uses a special tool with a rounded cutting edge designed to extract deep layers of tissue and sometimes subcutaneous fat. Punch biopsies are performed when the growth appears to have affected the dermis and when melanomas, inflammatory skin disorders, and carcinomas are suspected.
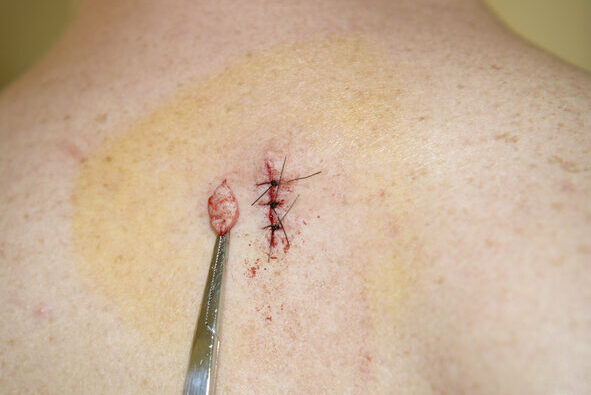
Excisional Biopsy
An excisional biopsy removes the entire skin growth and a small amount of surrounding healthy tissue. Excisional biopsies are the preferred approach for melanomas.
What Does a Skin Biopsy Procedure Involve?
During your consultation, your doctor will assess the growth and address your concerns. Additionally, your doctor will ask you about the length of time the growth has been present, additional symptoms, and your medical history. A full-body skin check might also be performed during the session.
If your doctor requires a skin biopsy before making a diagnosis, you might be given the option of scheduling the procedure at a later date if the condition isn’t believed to be urgent. However, if a skin cancer test is needed or you need a skin biopsy for a rash that appears to be worsening, a same-day outpatient biopsy might be recommended.
A skin biopsy typically involves the following:
Pre-biopsy Preparation
Before the biopsy, the dermatologist will sterilize the biopsy site with alcohol or another disinfectant and may apply a numbing agent to minimize discomfort during the procedure. The dermatologist will mark the area of the skin to be biopsied using a surgical pen or marker. This precaution is taken because some skin growths or lesions become difficult to identify when an anesthetic is injected.
The Skin Biopsy Procedure
Depending on the type of biopsy, the dermatologist will make a small incision or use a circular punch tool to remove the tissue sample. The choice of technique depends on the depth and size of the lesion being biopsied. Once the tissue is removed, the dermatologist will apply pressure or use an electrocautery device to control bleeding. A punch biopsy or excisional biopsy might require sutures to close the wound.
Post-procedure
After the biopsy, your doctor will bandage the site to protect the wound and promote healing. You will receive a set of wound care instructions to minimize the risk of complications.
When the specimen is collected, it is placed in a preservative solution to maintain the integrity of the tissue. It is then carefully labeled and sent to the pathology laboratory for analysis.
A dermatopathologist, a specialist in analyzing skin tissue, will process the sample and examine the specimen under a microscope. They look for specific features and changes that can help diagnose the skin condition accurately.
Once the analysis is complete, the dermatologist will evaluate the results and discuss the findings with you. Based on the diagnosis, appropriate treatment options will be recommended to address your specific skin condition.
Skin Biopsy FAQs
What Can a Skin Biopsy Detect?
A skin biopsy might be used to diagnose the following conditions:
- Skin cancer
- Skin infections
- Inflammatory skin conditions
- Autoimmune disorders
- Hair disorders
- Nail disorders
Sometimes, a skin biopsy is performed to monitor the progress or response to treatment of a known skin condition. By comparing biopsy results over time, doctors can assess the effectiveness of a particular therapy and make adjustments as needed.
How Painful is a Skin Biopsy?
A skin biopsy is typically nearly painless, though some patients might experience a mild pinch when a local anesthetic is injected.
After the procedure, you might experience some discomfort at the biopsy site, though this resolves within a few days and can generally be managed with drugstore pain relievers. Following postoperative wound care procedures will help minimize discomfort.
How Long Does a Skin Biopsy Take?
Skin biopsies usually take 15 minutes to complete, though the time may vary depending on the area to be sampled, its size, and the type of procedure being performed. When a large excisional biopsy is necessary, the procedure might take up to 30 minutes if suturing is necessary.
How Long do Skin Biopsy Results Take?
It is important to note that the time frame for receiving skin biopsy results can vary from case to case. Factors such as the situation’s urgency or the need for additional testing may affect the turnaround time. However, in general, it can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks to obtain the results of a skin biopsy.
It is best to consult your dermatologist for an accurate estimate of when the results will be available.
How Long Should You Keep a Skin Biopsy Covered?
The healing speed depends upon the type and location of the biopsy. Wounds on the lower extremities tend to heal more slowly than those on the face and torso.
You can expect to keep the biopsy site bandaged for at least 2-3 days. Generally, it might take several weeks for the wound to heal completely.
How Often Are Skin Biopsies Cancerous?
The vast majority of skin biopsy results do not discover life-threatening cancers.
According to a study published in 2017, roughly 44% of skin biopsies found malignancies, though only 1.4% were melanomas, the most dangerous type of skin cancer. Most skin cancers found during biopsy are localized and highly curable.
Can I Work Out After a Skin Biopsy?
It is best to avoid activities that could stretch or aggravate the biopsy site for at least one week after the procedure. The size and location of the wound will also be a factor in determining how long you must wait to resume your normal routine. Your doctor will provide post-care instructions specific to your case.
Can a Skin Biopsy Show Autoimmune Disease?
Biopsies can help diagnose autoimmune disorders that affect the skin, such as lupus or autoimmune blistering diseases. Doctors can identify specific immune system abnormalities contributing to these conditions by examining the skin tissue.
At Desert Valley Dermatology, we offer the Phoenix, AZ community access to state-of-the-art dermatologic care. We provide the latest diagnostic and treatment protocols for complex skin conditions, helping our diverse patient population manage and overcome a wide range of skin concerns.
