Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the United States, with nearly 10,000 new cases in the U.S. every day. At Desert Valley Dermatology, we specialize in identifying and treating a broad spectrum of skin cancers early, helping patients achieve the best possible outcomes.
It is estimated that one out of every five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. It is important to protect your skin from the sun and check for any skin cancer symptoms, including suspicious changes or skin growths. Early detection and treatment can save lives.
Fortunately, skin cancer is highly treatable when diagnosed early. Regular skin checks and self-exams can help to detect skin cancer in its early stages. The specialists at Desert Valley Dermatology offer state-of-the-art diagnostic tools and treatment modalities that give patients excellent results with minimal discomfort and downtime.
What are skin cancer risk factors?
While there are numerous skin cancer causes, the primary risk factors for developing skin cancer are the following:
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds
- Family history of skin cancer
- Having fair skin, freckles, and a tendency to burn rather than tan
- Weakened immune system
- Previous diagnosis of skin cancer
- History of radiation therapy
People who live in areas with high levels of ultraviolet radiation, such as high altitudes and areas closer to the equator, are also more likely to develop skin cancer. The best way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to minimize exposure to ultraviolet light from the sun and tanning beds, use sun protection, and have regular skin exams.
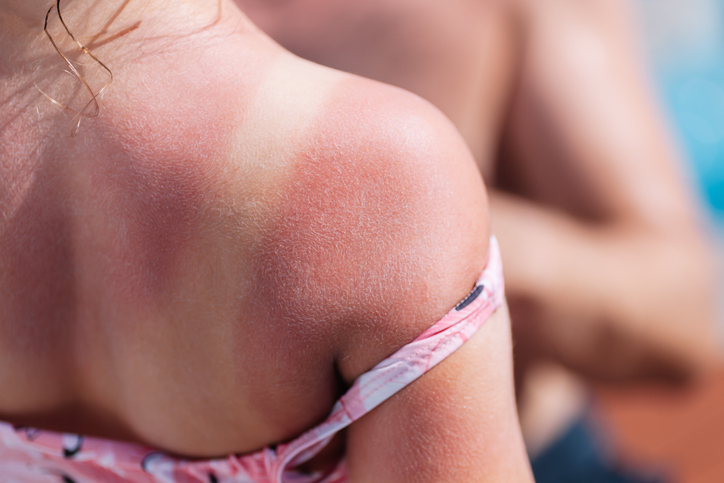

What does skin cancer look like when it first starts?
Skin cancer can present in many ways, so it might be difficult to recognize when it first starts.
Generally, skin cancer can begin with an abnormality in the form of a small spot, mole, discoloration, or lump on the skin. It may also be small and flat, or it might be raised and bumpy.
Any spot on the skin that does not heal or changes in appearance should be evaluated by a doctor to determine if it is skin cancer.
Common Skin Cancer Types
Skin cancer comes in numerous forms, each with different signs, symptoms, and outlooks. While the concept of skin cancer seems scary, it’s important to note that most skin cancers are highly treatable. At Desert Valley Dermatology, we screen for the following types of skin cancer.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, accounting for around 80% of all skin cancer cases. It can appear anywhere on the body, but most commonly on areas that have a lot of sun exposure.
Basal cell carcinoma usually appears as a raised, pearly bump or nodule on the skin. It may also be flat, scaly, or slightly elevated. The lesion can be pink, red, or flesh-toned and look like a sore that doesn’t heal.
Basal cell carcinoma is a slow-growing skin cancer that does not usually spread inside the body, but can be locally destructive. Treatment for basal cell carcinoma includes surgery, topical medications, and sometimes radiation. In some cases, cryotherapy may also be used.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is a skin cancer affecting the epidermis’s outermost layer. It is a widely seen form of skin cancer caused by heavy exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It typically appears as a hard, scaly, or crusty bump or patch on the skin and can be either red or brown.
Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for around 20% of all skin cancer cases. The condition can be easily treated when detected early but can be fatal if left unaddressed. Treatment often involves surgical removal of the cancerous tissue, and occasionally requires radiation and chemotherapy.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a form of skin cancer that is formed when the skin cells known as melanocytes mutate and grow aggressively. Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, accounting for nearly 100,000 skin cancer cases diagnosed in the U.S. annually. Of these, it is estimated that approximately 10,000 people will die of the condition in the same year.
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body, including the eyes, but is most commonly found on the face, arms, legs, and chest. It can occur in people of all ages, but it is more common in those with fair skin and those who are exposed to ultraviolet radiation, such as sunlight. Symptoms of melanoma include:
- Changes in the size or shape of a mole
- The appearance of a new mole or spot
- Changes in the color or texture of a mole
When evaluating a new or pre-existing mole, it is helpful to use the ABCDE criteria for mole evaluation.
A – Asymmetry. One half of the mole does not look like the other half.
B – Border. The mole may have an irregular, scalloped border.
C – Color. When there are variable colors within a mole
D – Diameter. Often larger than 6mm, typically the size of a pencil head eraser
E – Evolving. Any mole that changes in size, shape, or color should prompt an examination with your dermatologist.
If left untreated, melanoma can spread and become difficult to manage. To reduce the risk of developing melanoma, it is important to use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and avoid tanning.
Rare Skin Cancers
The above types of skin cancer are important to recognize, but numerous less well-known forms can be quite aggressive, so early vigilance is important. We offer screening and treatments for the following rare types of skin cancer.
Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma (CTCL)
Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma (CTCL) is a type of cancer that affects the skin’s T-cells, a category of white blood cells that helps the body fight infection. Some of the most common signs and symptoms include the following:
- Patches of itchy, scaly, or thickened skin
- Raised red rash all over the body
- Thickened skin on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands
- Plaques
- Skin discoloration
- Skin ulcers
- Swollen, painful lymph nodes
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Hair loss
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
CTCL is a rare kind of cancer, and it is estimated to affect less than 1 in 100,000 people yearly. It is usually diagnosed in older adults and is more common in men than women. While there is no cure for CTCL, treatment options are available to help slow the progression of the disease and manage the symptoms. These treatments may include topical creams, phototherapy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation.
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP)
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare form of cancer that affects the skin and forms under the skin’s surface. It is a type of soft tissue sarcoma that most commonly occurs in the chest, back, and abdomen. It is a slow-growing tumor and typically appears as a firm, reddish-brown nodule that is often mistaken for a cyst.
DFSP is a rare form of cancer, but due to the disease’s aggressive nature, early detection and prompt treatment are essential for successful outcomes. While DFSP is a serious medical condition, with the right treatment, it is highly manageable.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel Cell Carcinoma is a rare and aggressive skin cancer. It is a neuroendocrine tumor that usually develops in sun-exposed areas of the skin like the face, neck, and arms. It is caused by the Merkel Cell Polyomavirus (MCV).
Merkel Cell Carcinoma is more likely to occur in people with weakened immune systems and those who have had a lot of sun exposure. Symptoms of Merkel Cell Carcinoma include a painless, firm, and reddish-blue nodule on the skin that may grow quickly. Other symptoms are skin ulcerations, itching, and bleeding.
Sebaceous Carcinoma
Sebaceous carcinoma is an uncommon type of skin cancer that arises from the cells that make up the sebaceous glands. These glands are located in the skin, and they produce an oily substance called sebum. This form of cancer usually affects adults over the age of 40, and it typically appears as a painless lump on the eyelids or face. It can also appear in other areas of the body, such as the scalp, neck, and genital area.
Sebaceous carcinoma can develop in other parts of the body, and if left untreated, it is sometimes life-threatening. Signs and symptoms may include a painless lump on the skin, a lump that bleeds or oozes, redness, a scaly patch of skin, or a fast-growing lump.
